Abstract: In the context of global ecological degradation, scholars and practitioners have increasingly emphasized the interconnectedness of education and ecology, with particular attention given to the concept of ecological literacy. Over the past decades, numerous definitions, approaches, and conceptual frameworks have emerged for ecological literacy, each associating it with various meanings and methods. This broad scope is a significant characteristic of ecological literacy as it underscores its interdisciplinary nature. However, for stakeholders in the field of ecological literacy as well as related domains such as environmental education and sustainability education, this plurality of meanings has become problematic because it creates confusion and makes the concept difficult to work with. This article assesses the concept of ecological literacy to enhance the general understanding among researchers and practitioners. It is structured into four main sections: definition of the concept, early articulations, frameworks, and empirical research. Finally, the article concludes with a discussion on the implications of these findings for environmental educators.
Continue Reading
Abstract: One way to disrupt traditional Eurocentric teaching practices is through modifying curriculum in classes. Particularly, in an English Composition 101 course, an ongoing assignment called the Poetry Journal may assist students in thinking critically and reflexively. The concept was inspired by a high school English teacher, Brett Vogelsinger (2016), called “4 Reasons to Start Class with a Poem Each Day.” His four reasons: 1. Poems are short; 2. Poems are intense; 3. Poems connect (to other readings); 4. Poems inspire (writing). When building the assignment for a community college class, an instructor may make intentional (disruptive) choices for the poems. This article explores the project, which is grounded in culturally sustaining (Paris, 2021) and disruptive pedagogies (San Pedro, 2018)—both of which encourage the rethinking and dismantling of traditional Eurocentric-based instruction—and how the author (full-time faculty at a community college) applied said pedagogies to a specific in-class student activity to engage students in critical and reflexive thinking.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The Keepers of the Flame Initiative, now in its fifth year, is a dynamic partnership between cultural fire practitioners, UC Davis faculty, and a diverse study body. This experiential learning initiative at the University of California, Davis centers Indigenous Fire Workshops, focusing on cultural fire. By centering Indigenous science and teaching approaches, this initiative inherently becomes high impact. High Impact Practices (HIPs) are pivotal educational interventions that promote holistic student development and experiential learning. These practices encompass features such as setting appropriately high expectations, experiences with diverse people and circumstances, sustained student engagement over an extended period, meaningful interaction with faculty and peers, public demonstration of learning, real-world relevance of classroom learning, and structured opportunities for reflection. The Keepers of the Flame Initiative incorporates two types of powerful high impact practices: collaborative group projects and community-based learning. These educational practices significantly enrich student learning and particularly benefit historically underserved students as well as broader student populations. I analyze HIP features within the Keepers of the Flame Initiative using survey data gathered in winter 2023, while also delving into the importance of Indigenous-led educational approaches. Indigenous perspectives and educators are crucial in broadening educational approaches, providing a pathway to uphold sovereignty of diverse knowledge systems, and nurturing a sense of responsibility towards land stewardship and environmental justice.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Southern Arkansas University has developed the SOAR Sustainability Conference to spotlight current sustainability-related efforts. SOAR, representing the southern Arkansas region, was added to the conference name to signify the area of emphasis for the event. This spring conference event has been held in April of 2022 and 2023. The 2023 conference included over 50 presenters from academia, private businesses, government agencies, and volunteer organizations. Session topics were aligned with the critical components of sustainability education including anticipatory thinking, empathy, change of perspective, justice, responsibility, and ethics. Surveys were distributed to SOAR conference attendees to gauge their level of attitudes, knowledge, and behavior regarding sustainability issues. Responses were very positive overall, showing gains in attendees’ attitudes, knowledge, and behavior between 2022 and 2023. The behavior category showed the largest annual increase while knowledge gains over the same period were lower. Overall, the SOAR Sustainability Conference has shown success in engaging students and community stakeholders to take part in this effort to address sustainability-related challenges in the area.
Continue Reading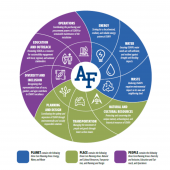
ABSTRACT: In this paper we offer an approach to sustainability-related education that can help students integrate the lessons they are learning in the classrooms to the type of real-world applications they will encounter in the workplace. We believe that by using our campus as a living-learning laboratory and engaging students in hands-on projects within a campus lab that directly contribute to one of their institution’s leading sustainability initiatives, we can unlock the highest levels of educational achievement and student satisfaction. We describe our course as intentionally designed because we have developed it with a specific purpose that goes beyond the stated learning objectives. Our course not only addresses recognized institutional and course-level educational outcomes, but also uses a community engagement approach that also directly supports important aspects of an enterprise-wide Sustainability Strategic Plan. We present relevant literature, highlight the significance of our approach to sustainability education, and describe its impact at our institution and in the community. We then offer detailed descriptions of our course’s activities, discuss lessons-learned and suggest future potential avenues of research and application. We hope this case study may prove to be an exemplar or a catalyst for other institutions of higher education as well as inspire further research aimed at improving sustainability education.
Continue Reading
Abstract: While the majority of today’s youth accept climate change as a factual phenomenon, many educators and their curricula lag behind with a continued emphasis on confronting climate skepticism and denial. This article highlights our experience teaching a course, Climate Change and Sustainability, in which we encountered disruptive objections to our lessons from students who believe climate change is happening and desperately want action. However, the all-or-nothing stance of these students stifled conversation, and their lack of engagement with various topics kept them uninformed. To address these issues, we recommend structuring classroom debate around consensus-building activities to practice solution-oriented communication.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This case study discusses the implementation of a park audit project with undergraduate college students in teacher education and public health programs. With a focus on drawing attention to the importance of urban green spaces in these two professional fields, the design of this project extended course activities into local parks. Students prepared to conduct park audits by engaging with course material focused on the importance of urban green spaces for individual health and children’s development, as well as inequities in access to high quality parks. The capstone of the course project was the audit of parks using the Community Parks Audit Tool (CPAT) in which each student assessed several parks in their local communities and documented their findings. This article discusses the contextual relevance of this project, its value in increasing attention to environmental considerations in the education and public health fields, as well as student responses to the implementation of the project in these specific classes.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The concept of sustainability has been gaining increasing attention worldwide, especially over the last 30 years. To foster sustainable development, education plays a crucial role. Higher education institutions have assumed the leading role in sustainability education and advocating sustainability. However, the literature that evaluates sustainability initiatives at higher education institutions is still fragmented and sparse, with existing studies often focusing on certain aspects of the sustainability initiatives. We designed a questionnaire that covers a broad spectrum of sustainability measures in the operation, curriculum, research, and outreach, which allowed us to investigate the perceived importance of those sustainability initiatives from the perspective of university community members including undergraduate students, graduate students, faculty, and staff at Texas State University in San Marcos. Our results indicated that the Texas State University campus community believes that the themes of Waste Management, Buildings & Infrastructure, and Water Use & Management were the most important themes. The campus community believed that Transportation and Academics are the least important themes. We also identified a set of action items under each theme the most and least important.
Continue ReadingAbstract: Actualization of the 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs) conceived by the United Nations in 2015 is a global challenge that may not be feasible in sub-Saharan Africa by the year 2030, except higher education play a committed role. There is need for higher education to embrace partnership and train people on the concepts of sustainability and sustainable development in the region. This paper presents a model center with curricular framework and partnership structure for the training. The Model Center for Sustainability Studies (MCSS) will enable partnerships with institutions in Africa and in advanced nations, thereby creating a global network for sustainability studies not found in sub-Saharan Africa. MCSS will train and certify public servants, government agencies, policymakers, entrepreneurs and personnel from organizations and students on aspects of the SDGs and sustainability science. It is important to add sustainability into environmental education and make environmental education a compulsory course in higher institutions and a secondary school certificate exam subject in sub-Saharan Africa. MCSS has 11 training modules that can be replicated anywhere in the world. Higher institutions in sub-Saharan Africa should follow this training perspective, to achieved SDGs, predicted 2040 against 2030.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Sustainability is a core value of Gen Z and is increasingly a focus of campus strategic plans. Undergraduate survey data can inform campus programming by increasing our understanding of student sustainability behaviors, knowledge, attitudes, and how these relate to student participation in curricular and cocurricular activities. Repeated surveys can track change over time in general and among underserved demographic segments of the student population. Here we evaluate the first in a series of biennial sustainability surveys that will guide planning at a mid-sized midwestern university in the USA. Our survey, modeled after existing surveys, was distributed to undergraduate students at the University of Minnesota Duluth (348 respondents) and collected demographic information including: college affiliation, year in school, gender, race/ethnicity, and campus residence. Our study showed that student knowledge scores were comparable to similar surveys at other institutions (66%) and the average attitude score was very high (88%). However, scores related to sustainability action were strikingly lower, indicating a gap between students’ understanding and acceptance of sustainability concepts and their willingness to engage, which we refer to as value-action gaps. When significant differences were detected between demographic groups, students who self-identified as female were more likely to have a higher sustainability score than students who identified as male and students who lived off campus were more likely to have a higher score than students who lived on campus. Other demographic results were mixed or not significant. We also noted a trend for students to score lower on questions related to business or economic sustainability and, similarly, for business students to score lower on sustainability questions overall than students in other colleges. Based on these baseline results, we provide recommendations to improve sustainability education and address the value-action gaps identified in this survey.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This article provides a case study of place-based sustainability education on the use of plastic bags in a wet market in Hong Kong. We organised two field trips and engaged 20 students in conducting both quantitative and qualitative research in the wet market to examine single-use plastic consumption. Our research has found that at least 1 million plastic bag is consumed on a daily basis in all the wet markets in the city of Hong Kong. Qualitatively, we found that some of the vendors may use plastic bags as a sale strategy and to engage with customers in conversations. In contrast to the conventional schooling that promote sustainability or plastic reduction in a very abstract sense, the place-based education we attempted aims to critically rethink the concept and knowledge of sustainability in ways that also empathize with the local tradition, and remain critical of modern corporate branding, and modernization discourse. The paper ends with a discussion on reflecting plastic use in traditional wet markets in contrast with chained supermarket shifting to more plastic pre-packages.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The West Virginia Climate Change Professional Development (WVCCPD) Project was developed in 2019 as an effort to engage West Virginia K-12 teachers and informal educators in climate change professional development to encourage learning and action. Started by astronomy educators who are passionate about climate change, the project has been an experiment that has iteratively grown each year. By bringing in social science experts, communication specialists, community activists, master teachers, and learning how to best support teachers and their students through misconceptions and empowering action, we have engaged over 130 W.Va. educators. WVCCPD represents a promising case study for how educators can come together across disciplines and institutions to build an engaging climate change learning community, even in West Virginia, an area that is known for fossil fuel extraction. We hope this paper informs other teacher education practitioners.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This case-study supports the implementation and social investment in university campus community gardens as an interdisciplinary resource for academic research, extra-curricular activities, and community building. Using a permaculture design model, the St. Lawrence University community permaculture garden in Canton, New York State exists to enhance the diverse academic curriculum and varied community engagement opportunities to provide experiential and interdisciplinary learning opportunities for students, faculty, staff, and remaining stakeholders. This case-study will focus on one of St. Lawrence University’s student-led clubs, its operations, history, and challenges (e.g., participant transience). Our findings suggest that campus permaculture gardens require adequate investment, including financial and academic support. The development of a conceptual seasonal and academic community calendar provides a fundamental framework for operations and governance. The sheer number of opportunities and broad capacity of the club and the presence of physical student space brings meaningful accessibility and community engagement. Over time, the club and garden has remained resilient due to a holistic approach which keeps the bigger picture in mind. Each year the club faces a variety of challenges and obstacles, yet such experiences have provided opportunity for adaptation and evolution. Recommendations can be used to support a replicable model for other educational environments and communities in both urban and rural areas, interested in developing a permaculture garden as a resource that improves social cohesion during a time of ecological fatigue, social unrest, the COVID-19 pandemic, and climate change.
Continue Reading
Abstract: I find it concerning, as a former elementary teacher and now a teacher educator, that not much attention is given to the preparation of new teachers on the environmental and social crisis of climate change. I have taught in two teacher preparation programs at public universities in the United States and understand the complexities, barriers, and limitations that these programs must contend with when trying to implement something new into an existing curriculum. In this paper I will describe my first attempt in navigating through the process of trying to include climate change education into a teacher preparation program. The focus of this initial effort was to understand the climate change literacy and self-efficacy towards teaching about climate change of the students in my elementary science teaching methods course.
Continue ReadingAbstract: In her narrative, Rioux argues for the significance of teaching place-based ecocomposition to diverse and multilingual writing students in order to emphasize and demonstrate the interconnectivity between all places and spaces that we inhabit despite human-made geographic boundaries. Addressing global issues with writers who represent various places around the globe enables writing students and instructors to hone in on the international nature of climate change while emphasizing the exigence that our natural context requires. Based on primary research, the author examines how teaching place-based ecocomposition to a uniquely diverse student group affects the writing students’ recognition of the interconnectivity of all places despite geographic location. Rioux explores how diverse environmental writing students perceive the effectiveness of a place-based course as it pertains to its objectives of helping students recognize their role within our extended environments, how to become more aware of the interconnectedness that combines and connects all places, and general environmental concerns that mark the Anthropocene. Providing pedagogical insights, Rioux also shares what the students find most effective in regards to course materials, design, and overall pedagogy, as it is imperative for our collective future to understand how to engage and motivate the next generation’s thinkers, writers, and Earth-dwellers.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Finding love and reciprocity in the garden during challenging times by growing community-based learning experiences.
Continue ReadingAbstract: Formal and nonformal educators help develop the environmental literacy (EL) of K-12 students, but do so in very different contexts. This paper describes educators’ views of their roles in developing student environmental literacy and barriers to that work. Educators with more advanced EL mentioned practices such as perspective taking and information evaluation. Many educators highlighted developing a connection – between students and the environment or between curriculum and students’ lives – as key to their work. The barriers identified reflect previous research, with nonformal educators also identifying access to student and peoples’ access to their sites as a major barrier.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This case study follows the eight-year development of an environmental anthropology course, beginning with my own failure as a teacher to provide students an adequate way of thinking and acting amid planetary crisis. It then turns to a diagnosis of three challenges students face when thinking about global ecological futures: (1) an inability to act, (2) an inability to imagine how an individual can make a difference, and (3) an inability to conjure an adequate sense of hope. For each of these challenges, I introduced a conceptual metaphor designed to help us think anew, where a conceptual metaphor is a trope that enables thinking about one conceptual domain in terms of another. The metaphor of wayfaring helped us overcome the conviction that one must become an expert before acting. The metaphor of seed planting helped us reimagine how an individual can contribute to larger-scale change. Finally, I introduce two new conceptual metaphors for thinking about hope amid planetary crisis—weedy invasions and broken jars. By working with these tropes, I propose an alternative way of thinking about hope that does not rely on a sense of optimism. Along the way, I make two broad arguments. First, thinking through novel conceptual metaphors, what I call metaphor work, is a worthwhile technique for approaching planetary crisis with students. Second, an undergraduate seminar is an excellent place to experiment with new ways of thinking about, and living in, the Anthropocene.
Continue ReadingAbstract: Sustainability educators are in a difficult spot. They must describe our unsustainable impacts on the environment and marginalized peoples, our growing understanding of how these impacts affect future generations and other species, and our failures to make the changes necessary to approach sustainability. At the same time they must avoid pushing students over an obscure tipping point where such information causes them to retreat into despair. For despair leads to inaction, which will only hasten the deterioration of planetary health. We propose two approaches to helping students avoid despair and strengthen their motivation for pursuing sustainable changes. One approach appeals to the motivational energy of hope and the other to the power of tranquil resolve described in Stoicism. We understand these approaches to be complementary. The skills of hope work well when we are pursuing long shot goals, while those of tranquil resolve aid when the achievement of our goals is beyond our own control. While the skills of hope are more aligned with our cultural norms and thus likely easier to teach, skills associated with a tranquil resolve can more powerfully (and lastingly) address the climate challenges we face. Pedagogical examples and strategies of these skills in action are offered throughout.
Continue Reading
Abstract: A partnership between a university and local arboretum was expanded to include the campus library as a collaborator. Instead of having sustainability-themed programming between the two institutions focus on just the environmental components of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a library brings attention to literacy and information access across all aspects of the partnership. We share two public programs held between our university and an arboretum with strong involvement by the library in the development and execution stages, thereby increasing the connections across the SDGs and progress towards the 2030 agenda.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Staff members play an important role in guiding students through living lab sustainability projects at Harvard University. Since there are significant opportunities for co-curricular learning in these settings, we created the “We Are All Educators” professional development workshop to empower those staff members to optimize and track student learning throughout these projects. In this case study, we will briefly summarize key principles of CCL and discuss its benefits as a tool for sustainability education in higher education. We will also describe our planning and implementation process for the workshop, the content of our training materials, and the results. Finally, we will end with key takeaways, as our workshop may be applicable to co-curricular learning in a variety of higher education contexts.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This research explores the role that place attachment and place meaning towards an urban farm play in predicting undergraduate students’ civic-mindedness, an important factor in sustainability and social change. In 2017 and 2018, three STEM courses at a private university in the Midwest incorporated a local urban farm as a physical and conceptual context for teaching course content and sustainability concepts. Each course included a four to six-week long place-based experiential learning (PBEL) module aimed at enhancing undergraduate STEM student learning outcomes, particularly place attachment, situated sustainability meaning-making (SSMM), and civic-mindedness. End-of-course place attachment, SSMM, and civic-mindedness survey data were collected from students involved in these courses and combined with institutionally provided demographic information. Place attachment and SSMM surveys, along with the course in which the students participated, were statistically significant predictors of students’ civic-mindedness score.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Industrial forms of food production and consumption are tied to environmental and socio-economic crises like climate change and social injustice. Changes in consumer behavior provide a lever to initiate transformations toward a more sustainable food system. One vehicle that is widely recognized as having the ability to encourage behavior change at large is education. Sustainability education has become increasingly popular over the past two decades, often being studied in innovative teaching-learning formats which employ transformative pedagogies that aim to foster critical consciousness through deep listening, dialogue, action, and reflection of students. However, classical teaching formats that employ more transmissive pedagogies, focused on delivery and mastery of content, have been comparatively little researched in the field of sustainability with regard to how they impact student behavior. Thus, this research aims to study if transmissive sustainability education can encourage university students to consume food more sustainably. To accomplish this, a case study with 12 undergraduate students in a food sustainability course was conducted. Mixed-methods data collection and analysis techniques, such as questionnaires and interviews, were utilized in order to track participants’ self-reported food consumption behaviors before, during, and after the course. Results suggest agreement among participants about the importance of course contents, but show no significant changes in their food consumption behaviors. The findings of this empirical study support the conclusion that imparting sustainability knowledge alone is insufficient to trigger behavior change.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Does the use of an interactive GIS web map significantly influence the level of sustainability stakeholder engagement at institutions of higher education? With over 1,000 institutions of higher education across the globe, the AASHE STARS report is one of the main tools available to sustainability professionals. For many institutions, the STARS report serves as a metric of sustainability progress and a source of new ideas and methods, while GIS provides a platform to display information within a context of systems, places, or times. Interactive web GIS allows for digital storytelling and can allow the user to explore specific information pertinent to their interests. This research explores potential links between the use of web GIS platforms and levels of campus engagement as measured by STARS.
Continue ReadingAbstract: I was slow in coming to see the desperate need of sustainability education, in part because of a missed opportunity in my field of outdoor adventure education (OAE). Although a burgeoning set of scholars agree that OAE is strategically placed to educate for sustainability, little change within our discipline has occurred. To encourage the transition, this paper has four central aims. First, I contextualize the implications at stake by summarizing recent scientific predictions around climate change. Second, I differentiate sustainable OAE into the sustainability of OAE (e.g., its practices, footprint size, etc.) and OAE for sustainability (e.g., curricula that promotes education about sustainability), noting that despite long-standing petitions to address both, progress has been made in neither. Third, I celebrate, with others, the inherent potential that OAE has to promote sustainability through its educating in natural environs, within living/learning communities, which utilize physical/sensory, affective and intellectual ways of knowing that inspire critical impulses. Fourth, I outline the central changes that need to occur in order to create sustainable OAE. The foremost change needed is for OAE programs to curricularly commit to promoting a sustainability worldview, including values, knowledge, dispositions, and agency related to environmental, social, and economic justice. However, change of this depth will require a revision of OAE course offerings that allow for multiple and prolonged participant engagement over time. Such engagement, then, necessitates that OAE shift its emphasis from remote and sublime landscapes, to programs that not only connect participants to the places in which they reside, but cultivate a care and affection for them. This appreciation can be created through a combination of adventurous learning and microadventures. In sum, “local landscapes, far more often, as a way of life” encapsulate the changes OAE might make in contribution to the global need of sustainability.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Sustainability education can productively focus on concepts and/or skills, each playing an important role in preparing students to promote sustainability in society. We describe here the skills-based curriculum in an environmental sustainability practicum designed for undergraduate students. Although our curriculum provides training in numerous relevant skills, we focus here on one in particular: scenario planning. Originally developed in the 1970s by Shell Oil to develop robust business strategies in the face of future uncertainties, scenario planning is applicable to any planning domain where future conditions may be driven by the outcome of critical unknowns. For example, planning for effective community resilience in the face of climate change may depend on the degree of government support for renewable energy systems. In this practicum, students work in teams of 3-4 on the same challenge: Assess a specified human-natural system for its vulnerability to climate change in the next 20 years and develop solutions that effectively increase the resilience of the system in the face of uncertainty.
Scenario planning involves six steps: (1) Identify driving forces for future changes; (2 and 3) Identify certainties and uncertainties for future conditions; (4) Rank uncertainties by the degree to which they might affect future conditions; (5) Create a 2×2 grid of possible future scenarios based on the two most influential uncertainties; and (6) Describe the future world in each of these four scenarios. Using creative ideation techniques developed by IDEO for their Human-Centered Design methodology, students then use these four scenarios as the basis for envisioning effective strategies for promoting resilience regardless of how the critical uncertainties unfold (adaptive planning) or for influencing uncertainties to increase the probability that preferred scenarios manifest.

Abstract: The experience and impacts of climate change are uneven across generations, income classes, cultural groups, and geographical locations. Efforts to document and understand such experiences and related perspectives are increasing. Particularly among student groups, there is much attention on understanding how children and teenagers perceive climate change. However, until now, such perspectives of graduate students have not been represented in the literature. We, thus, surveyed and spoke with graduate students from a Geography, Planning and Environment Program at Concordia University in Montreal / Tiohtià:ke, Quebec, Canada. As a sample of next-generation decision makers, they shared fears, concerns, and recommendations consisting of both bio-physical and socio-political scientific dimensions. They expressed interdisciplinary perspectives related to climate change vulnerability, mitigation, and adaptation as they relate to water and extreme weather. Their fears included uncertainties pertaining to climate and human behaviors, and the possibility of surpassing global carrying capacities that could result in irreversible and lethal disasters. Considerations involved recognizing the vulnerability of the climate system and of humans, with a focus on socio-political injustices. Students placed a strong focus on emerging opportunities, such as fostering community development and investing in innovative technologies. They recommended power shifts, through paradigm awareness and reformed policies, where currently vulnerable populations access more decision-making power. They suggested fostering interdisciplinary and international cooperation to integrate climate science, involving age-appropriate modelling programs, into school curricula, and learning about human positionality and from resilient populations. We consider wicked problems, psychological distancing, and climate literacy as influential concerns in shaping climate change contexts and literacy. Our methodology allowed research participants to guide the study’s questions and foci with the use of a survey, collectively-generated word collages, and a focus group. The activities prompted space for the group to practice roleplaying as decision makers. As gentle form of Participatory Action Research, the methods could guide other groups to reflect upon and document their perspectives.
Continue ReadingAbstract: While it is widely recognized that effectively addressing climate change requires a drastic reduction in carbon emissions, we nonetheless find ourselves in an impasse, unable to imagine nor bring about a post-carbon future. This is, in part, because climate change is not only a technological problem, but also a philosophical, cultural, and aesthetic problem—an existential crisis of thinking, or perhaps unthinking. To unthink the carbon regime, higher education must forge new thought models and educational platforms that operate in solidarity across disciplinary scales and territories. This report documents a collaborative course development process for a grant-funded transdisciplinary course entitled: Unthinking Oil: Public Architecture and the Post-Carbon Imaginary. In particular, we discuss a virtual Unthinking Oil Workshop held with students and faculty from a range of disciplines. The workshop provoked broad discussions regarding the role of higher education in addressing the many entanglements between climate change, society, and the built environment.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This paper describes the outcomes of a game designed to teach advanced leadership skills, specifically influence and negotiation strategies, to current and aspiring sustainability professionals at Virginia Tech’s Center for Leadership in Global Sustainability. In the game, students assume the role of a key stakeholder and practice principle-based negotiation, conflict management, consensus building, and related influence skills needed by professionals working on complex sustainable development challenges such as the transboundary resource issues
regarding hydropower and watershed management. We collected pre- and post- survey data to assess the effectiveness of the simulation in developing students’ negotiation and influence skills. Results suggest that the training helps students develop confidence in using influence and negotiation skills and feel more competent and better prepared to serve as leaders in the field.

Abstract: Predicted changes in climate have generated interest in strategies to mitigate emissions of greenhouse gases and increase education on the topic. Our study involved an instructor-led team of 19 biology undergraduate students that aimed to quantify tree carbon sequestered on 67 hectares of a university campus forest near Utica, New York, and estimate its monetary value as a carbon offset. We identified individual hardwood and conifer trees and measured diameter at breast height (DBH) of 343 trees within fifteen 0.04-hectare sample plots during a 3-week period. We estimated total campus forest carbon to be 7,678 Mg and annual sequestration to be 82 Mg C/year. We also found additional educational value of this voluntary field research project beyond traditional ecology field exercises. Campus managers could choose to count sequestered carbon as an offset to annual CO2 emissions from campus operations. Although our campus is not eligible to sell the accumulated carbon, we calculated a one-time offset to be worth $143,397 on the voluntary carbon trading market. Future studies could benefit from the efficient sampling methodology we used to quantify carbon contained in large forest areas and increased student learning from project-based field exercises.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Podcasts are increasing in popularity as an educational tool in recent years, but there remains a lack of podcasts that focus on climate change. The goal of this project was to create a series of audio files that address global warming solutions in the state of Pennsylvania, with each episode based upon a drawdown solution. Project Drawdown is a nonprofit organization that models how to reach “drawdown”— the future point in time when levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere stop climbing and start to steadily decline. This audio collection contains new and original podcasts addressing each Project Drawdown sector of global warming solutions, such as materials and waste, electricity generation, and land use. To highlight efforts in Pennsylvania, thirteen interviews were conducted with scientists, journalists, and professionals from organizations across the state, such as Feeding Pennsylvania, Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA), Philadelphia Green Roofs, StateImpact Pennsylvania, and Land Air Water Legal Solutions. Named Drawing Down in Pennsylvania, the podcast collection starts with an introductory episode, then eight episodes each corresponding with one of the Project Drawdown sectors, and wraps up with two additional episodes – one titled “Hope” with messages of optimism towards achieving warming solutions from the interviewees, and a special episode that focuses on The Pennsylvania State University and its efforts toward to drawdown. The audio collection is published online, together with corresponding transcripts and supplemental materials. It is hoped that these podcasts will help inform Pennsylvania residents to make choices and to take action for a sustainable future. For residents outside of Pennsylvania, these drawdown efforts can be applied to different populations and regions. The entire podcast series can be accessed at: https://sites.psu.edu/drawingdownpa/ and is suitable for middle school through college classrooms as well as general audiences.
Continue Reading
Abstract: In Fall 2017, Penn State Brandywine kicked off an initiative titled Sustainovation, emphasizing programming and community collaborations through sustainability and innovation. The campus identified Tyler Arboretum as a community partner to work with to assist in advancing their education and outreach goals. Students from across the campus came together at the beginning of the semester for an initial meeting to be introduced to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), to meet the community partner and to hear about the semester project of adding sustainability education to the arboretum’s fall festival Pumpkin Days. In addition, a validated survey from Biasutti & Frate (2017) was given to the students to define their attitudes towards sustainable development before working with this partner and the project. The survey addresses four sustainability constructs of Environment, Economy, Society, and Education. At the end of the semester, the same survey was given to student participants in this Sustainovation project for Tyler Arboretum. Aggregate data show that there is a statistically significant difference in student attitudes at a minimum 90% confidence level (t-test) for eight of the twenty survey statements in the constructs of Environment, Economy, and Society.
Continue Reading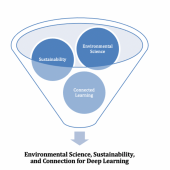
This comparative case study of teaching and learning experience explores connected learning design principles to improve engagement in higher education and weave sustainability practice into introductory environmental science curriculum through the integration of community, place, peer support, networking, and technology. For this study teaching and learning took place in multiple settings, online and in a brick-and-mortar classroom, and in students’ communities. We set out to ask: In what ways might the implementation of connected learning principles be used to improve engagement and weave sustainability into environmental science curriculum, broaden interest in science literacy, and encourage community action in introductory higher education courses? Comparative analysis and collaborative autoethnography methodologies were utilized to compare professor experiences for analysis and synthesis of patterns. Findings suggest that connected learning curriculum can broaden access to science, improve engagement, and help weave sustainability into a variety of courses by presenting students with relevant applied opportunities, connections and critical thinking about place and community, peer support and intergenerational connections, networking, and technology. Students can also gain a sense of agency and career relevance especially important to students who might otherwise feel they cannot “do science” or make a difference in a changing world. Lastly, this approach can improve instructors’ teaching experiences by relieving time and content constraints to incorporating sustainability into other course subjects as students submit more interesting passion-driven work, and are encouraged to network with and learn from individuals (family, community, and scientists) outside the classroom they may not have otherwise sought out.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Aldo Leopold’s classic essay, “Thinking Like a Mountain,” has been a touchstone of environmental ethics and sustainability education for over seventy years and continues to challenge and inspire wildlife ecology undergraduate students, and many more. But has it lost some power in the face of mounting evidence of accelerating damage and growing threats to the natural world, threatening biodiversity and human society on a global scale? Students and others now need another Leopold story, one that encapsulates an environmental ethic with a call for urgent action, a metaphor that urges not just change, but rapid transformation.
Continue ReadingLink to the Ecomedia Literacy Table of Contents Lopez et al. Editorial Overview JSE April 2020 Ecomedia Literacy PDF Forward from JSE Editor-in-Chief, Clare Hintz: The Journal of Sustainability Education marks its tenth anniversary year with an issue on Water Literacy (published in March) and this issue, Ecomedia Literacy. From a dream of several Ph.D. […]
Continue ReadingAbstract: The field of media education, emerging within the instrumental vision of modernity, has largely ignored its unspoken modernist assumptions. In this article, we argue the time has come to fully engage an embodied view of media from an evolutionary, ecological perspective—what we might call ecological modernism. This is a perspective that views media as evolving mediations through various material/technical practices, where body knowledge, rather than some idea of objective reality, is understood as the empirical ground for how we come to make sense of ourselves and the world. The focus is then shifted from the problem of subject versus object relationships to how subjects and objects are mutually constitutive. By extension, the juxtaposition of the concept of citizen with the body clarifies yet another crucial dimension of the embodied perspective. Two examples of “citizen”-based media education projects are briefly reviewed from this ecological modernist perspective in order to consider the implications of resituating grounded citizen-oriented media education.
Continue ReadingAmerica is falling behind the rest of the world in science and math. There is therefore, a renewed emphasis on STEM subjects (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math). But while mastery of STEM subjects is essential to the functioning of society, we’ve neglected some other areas that are at least as important, if not more so. But without an equal commitment to comprehensive civics education — an examination of subjects that touch on the relationships between people, government, the economy, and media — all the technical know-how in the world will be for naught. The author suggests a renewed focus on MESH education, which stands for Media Literacy, Ethics, Sociology, and History. Because if these are not given equal attention, we could end up with incredibly bright and technically proficient people who lack all capacity for democratic citizenship.
Continue ReadingAbstract: In recent years, media scholars and educators have made an effort to address ecological issues in their work. Ecomedia literacy adapts the principles and practices of the media literacy movement in order to prepare the public to critically engage with the relationship between media and the environment. However, this article argues that the philosophical frameworks, on which existing approaches to media literacy education are founded, are limited. The field’s reliance on traditions of constructivism and cultural studies allows learners to engage with ideas, but not things. The article argues that an ecomedia literacy that draws from speculative realism—in particular, in recognizing the reality of non-human things, emphasizing materiality, and challenging the nature/culture divide—will more effectively prepare the public to critically engage and practically respond to pressing ecological issues such as climate change.
Continue Reading
This essay describes a series of interdisciplinary projects addressing environmental issues in Florida where faculty and students from different departments collaborate on complex problems and produce multimedia work aimed at reaching a public audience. Through a series of brief case studies, a model of interdisciplinary experiential education emerges, providing a pathway forward for other faculty to create community engaged projects that have real world impacts.
Continue Reading
Transformative sustainable pedagogy and public intellectual work share the same aims and guideposts, including upholding higher education’s foundational intentions of fostering moral character in tomorrow’s leaders. Radical modes of sustainable education, including regenerative pedagogy, which tends to the global shift to restore, respect, and regenerate ecological and societal balance, and inside-out pedagogy, which helps learners take their inner seeds, sprouts, and blossoms of good ecocultural intentions to stages of external fruition, speak both to educating learners and engaging the public. If pedagogues aim to encourage students to put beliefs into action and be leading voices in ethically addressing today’s pressing environment and society problems, this may require role modeling by having the courage to do so themselves. In these contexts, the author relates her own experiences speaking for Extinction Rebellion as an illustration of expanding notions of what it means to be a sustainability educator today.
Continue ReadingThis editorial overview provides an introduction to this special Journal of Sustainability (JSE) issue devoted to water and climate change, which is being released during United Nations World Water Day 2020. The article contextualizes some of the water security risks that are exacerbated by climate change, such as increasing floods and droughts. This piece further provides a brief overview of the articles in the special water and climate issue of the JSE.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Part Two of a two-article series describes water conservation through graywater use and rainwater harvesting. Sustainable methods of heating water for a recirculating shower, and potential methods for water filtration and purification are presented. Also addressed is the feasibility of sustainable showering alternatives. An opportunity for educators and students to collaborate in the development of an off-grid recirculating shower is provided as well.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Part One of a two-part article outlines a brief history of showering and questions current showering practices. Current global levels of water use and availability are discussed, plus water use in the United States, relative to Americans’ frequency of showering. The energy requirements for cities to provide clean water is outlined as well as the carbon dioxide emissions that are subsequently released during water delivery and wastewater disposal. In Part Two, water conservation through graywater use and rainwater harvesting is described, and sustainable methods of heating water are offered. Possible methods for water filtration and purification are presented. The feasibility of alternatives for a more sustainable shower is addressed. Both articles conclude with an invitation to students and instructors to collaborate with the author to construct a prototype of an off-grid recirculating shower.
Continue Reading
Abstract
On campuses across the world, faculty, staff, and administrators continue to wrestle with how best to foster a stronger sense of belonging and community among first-year college students. Research in the field of education for sustainability (EfS) suggests that utilizing a cohort-based approach to sustainability education can lead to a number of positive outcomes for participating students and the broader campus culture. Meanwhile, student affairs research demonstrates the value of living/learning communities (LLCs) in supporting undergraduate students as they transition to college. This paper showcases the experience of Hobart and William Smith Colleges in implementing a sustainability-themed LLC on its campus, highlighting how one institution is utilizing sustainability education to build community among first-year college students.
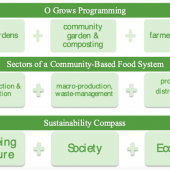
Abstract: This program feature documents our reflections on how the work of O Grows, is, or more accurately has become, increasingly sustainability-oriented. O Grows is a non-profit, community-university partnership with the mission to leverage the local capacity in service of community food needs. Specifically, we focus here on how engagement with an increasing number of sectors of the local food system, as we work toward this mission, has demonstrated a commensurate increase in alignment with the cardinal directions of the sustainability compass—attention to Nature, Society, Economy, and Wellbeing. We have realized, as O Grows has evolved, that keeping the program going and attending to sustainability are one and the same. As such, we argue the sustainability compass is a useful heuristic not only for reflection after-the-fact but also for partnership planning.
Continue ReadingSustainable development and creative thinking have become central aspects of Higher Education in today’s multidisciplinary world. With the balance between learning and teaching priorities in mind, the Design Academy, Sichuan Fine Arts Institute and School of Design, Jiangnan University incorporated the author’s newly evolved teaching methodology — 3Ac: ‘Acknowledgment, Action and Accountability’ model of sustainable development and creativity — into its taught programs at all levels. The 3Ac model is a formative learning method for building the capabilities of individuals to create changes toward sustainable development. This paper first defines the 3Ac design methodology (Acknowledgment, Action, and Accountability) in the context of sustainable development and education: Acknowledgment is the appreciation and recognition of the importance of sustainable development in the face of global challenges, with a particular focus on team effort, co-design and sharing findings and practices. Action is the establishment of design strategy and action plans that consider not only the importance of intentions, goals, affordable and reachable resources but also a clear road map for achieving maximum efficiency when tackling the most challenging tasks. Accountability deals with a growing understanding of the benefits of working together to tackle global challenges such as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) practices. The framework aims to develop students’ capabilities through case studies of undergraduate, graduate and continuing professional development of young designers. Based on evidence from the feedback and evaluation of action research, the research team plans to further refine the 3Ac design teaching methodology and create a model that can be implemented and scaled effectively with collaborative partners from the community, business and local government.
Continue Reading
Breaking though to millennials in the classroom is becoming an important objective for all educators. These students demand more from their learning experiences and many traditional education techniques are often ineffective. One technique that holds potential is “Flip” education, a unique active learning approach. Although Flip is normally associated with the hard sciences, this paper presents a case study that demonstrates its effectiveness in the social sciences, specifically an upper division undergraduate environmental/sustainability planning class. Two important takeaways from this study include: 1) that teaching must be more student-centered, allowing students to take more control of their own education as assigned material be available before the fixed class time so as to allow class time for more active learning; and 2) Students report improved learning when Flip experiential methods are used in conjunction with some form of standard professor lectures.
Continue Reading
Abstract: A United Nations international collaboration between the Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) and the Principles for Responsible Management Education (PRME) resulted in the creation of Sulitest® (aka Sustainability Literacy Test) an open, online training and assessment tool freely available to higher education institutions globally. This study analyzes the effectiveness of the newly developed Sulitest® to not only measure sustainability literacy of higher education student populations, but also act as a catalyst for boosting affective learning outcomes by: (a) generating interest in sustainability-related issues, (b) improving sustainability-related understandings, and (c) enhancing students’ interests in the subject matter. In order to do so we present a two-phase, exploratory mixed-method pilot study. Preliminary results from this pilot study reveal Sulitest is a useful tool for not only assessing sustainability literacy but also spurring student interests and motivations in sustainability-related subject matters. Findings, discussion and limitations are provided.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Students are transformed when they realize that their theory-based actions have real and meaningful impact. Student learning outcomes are enhanced when they realize this impact. This is important, because the topic of sustainability involves a huge amount of grim data about the state of the planet and our impending demise; and an urgent call for action to make positive impact. To enable my MBA students to take action, I designed an experiential, action-research and transformational pedagogical approach; and a mixed-methods study to assess if/ how students engaged with, and learned or cared about sustainability when it was delivered at the level of personal impact and personal action. I found that making sustainability personal did not cause alienation, but did significantly contribute to learning and caring in all students in the course. However, students’ comfort with uncertainty moderated their perceptions of learning, which provides insight for how to improve the course in the future.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This paper describes and explains findings from an exploratory, interpretative qualitative case study that examined how a residential graduate program in science education, based in a wilderness area, supported the development of citizen educators. Data collection over a three-year period included 16 in-depth interviews with administrators, faculty, and graduate students; observations of class activities and campus community meetings; and document analysis of curriculum materials. Analysis of the data revealed how the culture of the campus community encouraged students to become citizen educators.
Continue Reading