Abstract: In the context of global ecological degradation, scholars and practitioners have increasingly emphasized the interconnectedness of education and ecology, with particular attention given to the concept of ecological literacy. Over the past decades, numerous definitions, approaches, and conceptual frameworks have emerged for ecological literacy, each associating it with various meanings and methods. This broad scope is a significant characteristic of ecological literacy as it underscores its interdisciplinary nature. However, for stakeholders in the field of ecological literacy as well as related domains such as environmental education and sustainability education, this plurality of meanings has become problematic because it creates confusion and makes the concept difficult to work with. This article assesses the concept of ecological literacy to enhance the general understanding among researchers and practitioners. It is structured into four main sections: definition of the concept, early articulations, frameworks, and empirical research. Finally, the article concludes with a discussion on the implications of these findings for environmental educators.
Continue Reading
Abstract: One way to disrupt traditional Eurocentric teaching practices is through modifying curriculum in classes. Particularly, in an English Composition 101 course, an ongoing assignment called the Poetry Journal may assist students in thinking critically and reflexively. The concept was inspired by a high school English teacher, Brett Vogelsinger (2016), called “4 Reasons to Start Class with a Poem Each Day.” His four reasons: 1. Poems are short; 2. Poems are intense; 3. Poems connect (to other readings); 4. Poems inspire (writing). When building the assignment for a community college class, an instructor may make intentional (disruptive) choices for the poems. This article explores the project, which is grounded in culturally sustaining (Paris, 2021) and disruptive pedagogies (San Pedro, 2018)—both of which encourage the rethinking and dismantling of traditional Eurocentric-based instruction—and how the author (full-time faculty at a community college) applied said pedagogies to a specific in-class student activity to engage students in critical and reflexive thinking.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The Keepers of the Flame Initiative, now in its fifth year, is a dynamic partnership between cultural fire practitioners, UC Davis faculty, and a diverse study body. This experiential learning initiative at the University of California, Davis centers Indigenous Fire Workshops, focusing on cultural fire. By centering Indigenous science and teaching approaches, this initiative inherently becomes high impact. High Impact Practices (HIPs) are pivotal educational interventions that promote holistic student development and experiential learning. These practices encompass features such as setting appropriately high expectations, experiences with diverse people and circumstances, sustained student engagement over an extended period, meaningful interaction with faculty and peers, public demonstration of learning, real-world relevance of classroom learning, and structured opportunities for reflection. The Keepers of the Flame Initiative incorporates two types of powerful high impact practices: collaborative group projects and community-based learning. These educational practices significantly enrich student learning and particularly benefit historically underserved students as well as broader student populations. I analyze HIP features within the Keepers of the Flame Initiative using survey data gathered in winter 2023, while also delving into the importance of Indigenous-led educational approaches. Indigenous perspectives and educators are crucial in broadening educational approaches, providing a pathway to uphold sovereignty of diverse knowledge systems, and nurturing a sense of responsibility towards land stewardship and environmental justice.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Southern Arkansas University has developed the SOAR Sustainability Conference to spotlight current sustainability-related efforts. SOAR, representing the southern Arkansas region, was added to the conference name to signify the area of emphasis for the event. This spring conference event has been held in April of 2022 and 2023. The 2023 conference included over 50 presenters from academia, private businesses, government agencies, and volunteer organizations. Session topics were aligned with the critical components of sustainability education including anticipatory thinking, empathy, change of perspective, justice, responsibility, and ethics. Surveys were distributed to SOAR conference attendees to gauge their level of attitudes, knowledge, and behavior regarding sustainability issues. Responses were very positive overall, showing gains in attendees’ attitudes, knowledge, and behavior between 2022 and 2023. The behavior category showed the largest annual increase while knowledge gains over the same period were lower. Overall, the SOAR Sustainability Conference has shown success in engaging students and community stakeholders to take part in this effort to address sustainability-related challenges in the area.
Continue Reading
ABSTRACT: In this paper we offer an approach to sustainability-related education that can help students integrate the lessons they are learning in the classrooms to the type of real-world applications they will encounter in the workplace. We believe that by using our campus as a living-learning laboratory and engaging students in hands-on projects within a campus lab that directly contribute to one of their institution’s leading sustainability initiatives, we can unlock the highest levels of educational achievement and student satisfaction. We describe our course as intentionally designed because we have developed it with a specific purpose that goes beyond the stated learning objectives. Our course not only addresses recognized institutional and course-level educational outcomes, but also uses a community engagement approach that also directly supports important aspects of an enterprise-wide Sustainability Strategic Plan. We present relevant literature, highlight the significance of our approach to sustainability education, and describe its impact at our institution and in the community. We then offer detailed descriptions of our course’s activities, discuss lessons-learned and suggest future potential avenues of research and application. We hope this case study may prove to be an exemplar or a catalyst for other institutions of higher education as well as inspire further research aimed at improving sustainability education.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The concept of sustainability has been gaining increasing attention worldwide, especially over the last 30 years. To foster sustainable development, education plays a crucial role. Higher education institutions have assumed the leading role in sustainability education and advocating sustainability. However, the literature that evaluates sustainability initiatives at higher education institutions is still fragmented and sparse, with existing studies often focusing on certain aspects of the sustainability initiatives. We designed a questionnaire that covers a broad spectrum of sustainability measures in the operation, curriculum, research, and outreach, which allowed us to investigate the perceived importance of those sustainability initiatives from the perspective of university community members including undergraduate students, graduate students, faculty, and staff at Texas State University in San Marcos. Our results indicated that the Texas State University campus community believes that the themes of Waste Management, Buildings & Infrastructure, and Water Use & Management were the most important themes. The campus community believed that Transportation and Academics are the least important themes. We also identified a set of action items under each theme the most and least important.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This paper reports part of a larger study on the development of systems thinking skills in German 7th grade comprehensive school students regarding the climate. Research has shown a fragmented understanding of climate change among students that hardly accounts for the dynamic interrelations in the climate system and may pose a barrier in understanding adaptation and mitigation strategies (Shepardson et al., 2017, 2011, Calmbach 2016). While much is known the impact of short-term interventions on the general system understanding of students, what is lacking to date is 1) a specific intervention on climate system understanding and 2) insights into the process of developing system understanding in students. Helpful insights in this context come from Conceptual Development theories for they allow the development of systemic thinking to be viewed in terms of conceptual expansion or conceptual change. Starting from these desiderates, a teaching-learning sequence was developed based on the SYSDENE model of system competence (Frischknecht et al. 2008). In the sequence young learners systematically link experiences from formal science education with the experiences at three non-formal learning environments. A mixed-methods approach was used to explore the impact of this 3-month sequence on 19 7th grade students. A written pre-/post-test suggested a significant improvement in Climate System Reconstruction for the group (pre-test Median = 6.75 vs. post-test Median = 12.5, Wilcoxon Test: p = .003, r = .82). However, a qualitative analysis of classroom conversations, interviews and concept maps indicated that cognitive development toward a higher level of system thinking was neither continuous nor did every student reach it. Moreover, the SYSDENE model’s Competence Area “Describe System Model” proves critical. Being able to describe the main climate system factors is not sufficient, one also needs to be able to distinct weather from climate and grasp several scientific concepts related to the climate (e.g. greenhouse effect, water cycle, evaporation, reflection) in order to understand climate as a system.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Sustainability is a core value of Gen Z and is increasingly a focus of campus strategic plans. Undergraduate survey data can inform campus programming by increasing our understanding of student sustainability behaviors, knowledge, attitudes, and how these relate to student participation in curricular and cocurricular activities. Repeated surveys can track change over time in general and among underserved demographic segments of the student population. Here we evaluate the first in a series of biennial sustainability surveys that will guide planning at a mid-sized midwestern university in the USA. Our survey, modeled after existing surveys, was distributed to undergraduate students at the University of Minnesota Duluth (348 respondents) and collected demographic information including: college affiliation, year in school, gender, race/ethnicity, and campus residence. Our study showed that student knowledge scores were comparable to similar surveys at other institutions (66%) and the average attitude score was very high (88%). However, scores related to sustainability action were strikingly lower, indicating a gap between students’ understanding and acceptance of sustainability concepts and their willingness to engage, which we refer to as value-action gaps. When significant differences were detected between demographic groups, students who self-identified as female were more likely to have a higher sustainability score than students who identified as male and students who lived off campus were more likely to have a higher score than students who lived on campus. Other demographic results were mixed or not significant. We also noted a trend for students to score lower on questions related to business or economic sustainability and, similarly, for business students to score lower on sustainability questions overall than students in other colleges. Based on these baseline results, we provide recommendations to improve sustainability education and address the value-action gaps identified in this survey.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The contribution first outlines the state of research on the relatively new Fridays for Future (FFF) movement and categorises first studies particularly from a German perspective, to provide a basis for a further differentiation in this field of research. In this context, fundamental aspects of the movement are presented. The self-concept of the German Fridays for Future movement in terms of a young protest movement with a global orientation is then compared against the educational tasks stipulated in the school legislation of the federal states (Bundesländer) with their societal-educational objectives. The contribution focuses on the question in how far the self-concept of the German branch of the FFF movement as an international protest movement and the activists’ engagement for climate protection and political participation is reflected in the educational objectives stipulated in school legislation. Statements are analysed regarding climate and environmental protection, participation and democracy and transnational references in the school legislation. A link can be found between the self-concept of the Fridays for Future movement and school legislation, but this does not resolve the conflict between the school strikes and compulsory schooling – a conflict that is intended by FFF to highlight the perceived urgency of the cause. Schools, educational administrators and educational policymakers are thereby urged to take a stance.
Continue Reading
Abstract: I find it concerning, as a former elementary teacher and now a teacher educator, that not much attention is given to the preparation of new teachers on the environmental and social crisis of climate change. I have taught in two teacher preparation programs at public universities in the United States and understand the complexities, barriers, and limitations that these programs must contend with when trying to implement something new into an existing curriculum. In this paper I will describe my first attempt in navigating through the process of trying to include climate change education into a teacher preparation program. The focus of this initial effort was to understand the climate change literacy and self-efficacy towards teaching about climate change of the students in my elementary science teaching methods course.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Gaining a better understanding of human behavior change is vital to encouraging individuals to adopt an environmentally sustainable lifestyle and to the long-term goal of preserving nature. To explore how life experiences lead to the adoption of environmentally sustainable behaviors, this author turned to autoethnography. Through this reflective method, the author examines their development of environmental identity and their experiences with nature, as they relate to major concepts within the field of conservation psychology, such as ecological literacy, Theory of Planned Behavior, and connection to nature. Leading concepts concerning environmental identity in the conservation psychology literature suggest a very specific pathway for developing environmental identity, and thus pro-environmental behaviors, including experience in nature from a young age, the presence of an environmental mentor, and access to environmental literature. However, the author reveals that there may be other pathways to development of environmental identity, which include virtual environmental mentors (e.g., nature TV show hosts), environmental media (e.g., magazines, documentaries, and internet sources), and other methods of driving emotional connection to nature (e.g., sense of place). Alongside the author, the reader will have the opportunity to consider their environmental experiences and factors influencing their environmental identity, in relation to these major concepts within conservation psychology.
Continue ReadingAbstract: Formal and nonformal educators help develop the environmental literacy (EL) of K-12 students, but do so in very different contexts. This paper describes educators’ views of their roles in developing student environmental literacy and barriers to that work. Educators with more advanced EL mentioned practices such as perspective taking and information evaluation. Many educators highlighted developing a connection – between students and the environment or between curriculum and students’ lives – as key to their work. The barriers identified reflect previous research, with nonformal educators also identifying access to student and peoples’ access to their sites as a major barrier.
Continue ReadingAbstract: Sustainability educators are in a difficult spot. They must describe our unsustainable impacts on the environment and marginalized peoples, our growing understanding of how these impacts affect future generations and other species, and our failures to make the changes necessary to approach sustainability. At the same time they must avoid pushing students over an obscure tipping point where such information causes them to retreat into despair. For despair leads to inaction, which will only hasten the deterioration of planetary health. We propose two approaches to helping students avoid despair and strengthen their motivation for pursuing sustainable changes. One approach appeals to the motivational energy of hope and the other to the power of tranquil resolve described in Stoicism. We understand these approaches to be complementary. The skills of hope work well when we are pursuing long shot goals, while those of tranquil resolve aid when the achievement of our goals is beyond our own control. While the skills of hope are more aligned with our cultural norms and thus likely easier to teach, skills associated with a tranquil resolve can more powerfully (and lastingly) address the climate challenges we face. Pedagogical examples and strategies of these skills in action are offered throughout.
Continue Reading
Abstract: A brief history of climatological science sets the stage for understanding the rise of the greenhouse gas thesis. That science is true as far as it goes, justifying our confidence, but it is an incomplete assessment of climatic systems. We have spent 40 years accepting the “pot lid” as the cause of the pot boiling over. That the “sun-warmed surface” impacts climate has been known for nearly 200 years. But greenhouse science failed to incorporate that and other scientific findings on urbanism, water cycles, and land management practices. To remedy this, I propose a broad climatic paradigm to address the actual cause of warming and provide a far more hopeful future with ample opportunities to resolve over-heating more completely, locally, and in a matter of months, years, or maybe decades, instead of centuries. Lastly, I discuss the significance of paradigm change, a new approach, and an expanded curriculum as challenges to sustainability education.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This research explores the role that place attachment and place meaning towards an urban farm play in predicting undergraduate students’ civic-mindedness, an important factor in sustainability and social change. In 2017 and 2018, three STEM courses at a private university in the Midwest incorporated a local urban farm as a physical and conceptual context for teaching course content and sustainability concepts. Each course included a four to six-week long place-based experiential learning (PBEL) module aimed at enhancing undergraduate STEM student learning outcomes, particularly place attachment, situated sustainability meaning-making (SSMM), and civic-mindedness. End-of-course place attachment, SSMM, and civic-mindedness survey data were collected from students involved in these courses and combined with institutionally provided demographic information. Place attachment and SSMM surveys, along with the course in which the students participated, were statistically significant predictors of students’ civic-mindedness score.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Industrial forms of food production and consumption are tied to environmental and socio-economic crises like climate change and social injustice. Changes in consumer behavior provide a lever to initiate transformations toward a more sustainable food system. One vehicle that is widely recognized as having the ability to encourage behavior change at large is education. Sustainability education has become increasingly popular over the past two decades, often being studied in innovative teaching-learning formats which employ transformative pedagogies that aim to foster critical consciousness through deep listening, dialogue, action, and reflection of students. However, classical teaching formats that employ more transmissive pedagogies, focused on delivery and mastery of content, have been comparatively little researched in the field of sustainability with regard to how they impact student behavior. Thus, this research aims to study if transmissive sustainability education can encourage university students to consume food more sustainably. To accomplish this, a case study with 12 undergraduate students in a food sustainability course was conducted. Mixed-methods data collection and analysis techniques, such as questionnaires and interviews, were utilized in order to track participants’ self-reported food consumption behaviors before, during, and after the course. Results suggest agreement among participants about the importance of course contents, but show no significant changes in their food consumption behaviors. The findings of this empirical study support the conclusion that imparting sustainability knowledge alone is insufficient to trigger behavior change.
Continue ReadingAbstract: I was slow in coming to see the desperate need of sustainability education, in part because of a missed opportunity in my field of outdoor adventure education (OAE). Although a burgeoning set of scholars agree that OAE is strategically placed to educate for sustainability, little change within our discipline has occurred. To encourage the transition, this paper has four central aims. First, I contextualize the implications at stake by summarizing recent scientific predictions around climate change. Second, I differentiate sustainable OAE into the sustainability of OAE (e.g., its practices, footprint size, etc.) and OAE for sustainability (e.g., curricula that promotes education about sustainability), noting that despite long-standing petitions to address both, progress has been made in neither. Third, I celebrate, with others, the inherent potential that OAE has to promote sustainability through its educating in natural environs, within living/learning communities, which utilize physical/sensory, affective and intellectual ways of knowing that inspire critical impulses. Fourth, I outline the central changes that need to occur in order to create sustainable OAE. The foremost change needed is for OAE programs to curricularly commit to promoting a sustainability worldview, including values, knowledge, dispositions, and agency related to environmental, social, and economic justice. However, change of this depth will require a revision of OAE course offerings that allow for multiple and prolonged participant engagement over time. Such engagement, then, necessitates that OAE shift its emphasis from remote and sublime landscapes, to programs that not only connect participants to the places in which they reside, but cultivate a care and affection for them. This appreciation can be created through a combination of adventurous learning and microadventures. In sum, “local landscapes, far more often, as a way of life” encapsulate the changes OAE might make in contribution to the global need of sustainability.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The experience and impacts of climate change are uneven across generations, income classes, cultural groups, and geographical locations. Efforts to document and understand such experiences and related perspectives are increasing. Particularly among student groups, there is much attention on understanding how children and teenagers perceive climate change. However, until now, such perspectives of graduate students have not been represented in the literature. We, thus, surveyed and spoke with graduate students from a Geography, Planning and Environment Program at Concordia University in Montreal / Tiohtià:ke, Quebec, Canada. As a sample of next-generation decision makers, they shared fears, concerns, and recommendations consisting of both bio-physical and socio-political scientific dimensions. They expressed interdisciplinary perspectives related to climate change vulnerability, mitigation, and adaptation as they relate to water and extreme weather. Their fears included uncertainties pertaining to climate and human behaviors, and the possibility of surpassing global carrying capacities that could result in irreversible and lethal disasters. Considerations involved recognizing the vulnerability of the climate system and of humans, with a focus on socio-political injustices. Students placed a strong focus on emerging opportunities, such as fostering community development and investing in innovative technologies. They recommended power shifts, through paradigm awareness and reformed policies, where currently vulnerable populations access more decision-making power. They suggested fostering interdisciplinary and international cooperation to integrate climate science, involving age-appropriate modelling programs, into school curricula, and learning about human positionality and from resilient populations. We consider wicked problems, psychological distancing, and climate literacy as influential concerns in shaping climate change contexts and literacy. Our methodology allowed research participants to guide the study’s questions and foci with the use of a survey, collectively-generated word collages, and a focus group. The activities prompted space for the group to practice roleplaying as decision makers. As gentle form of Participatory Action Research, the methods could guide other groups to reflect upon and document their perspectives.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This paper describes the outcomes of a game designed to teach advanced leadership skills, specifically influence and negotiation strategies, to current and aspiring sustainability professionals at Virginia Tech’s Center for Leadership in Global Sustainability. In the game, students assume the role of a key stakeholder and practice principle-based negotiation, conflict management, consensus building, and related influence skills needed by professionals working on complex sustainable development challenges such as the transboundary resource issues
regarding hydropower and watershed management. We collected pre- and post- survey data to assess the effectiveness of the simulation in developing students’ negotiation and influence skills. Results suggest that the training helps students develop confidence in using influence and negotiation skills and feel more competent and better prepared to serve as leaders in the field.
Abstract: In recent years, media scholars and educators have made an effort to address ecological issues in their work. Ecomedia literacy adapts the principles and practices of the media literacy movement in order to prepare the public to critically engage with the relationship between media and the environment. However, this article argues that the philosophical frameworks, on which existing approaches to media literacy education are founded, are limited. The field’s reliance on traditions of constructivism and cultural studies allows learners to engage with ideas, but not things. The article argues that an ecomedia literacy that draws from speculative realism—in particular, in recognizing the reality of non-human things, emphasizing materiality, and challenging the nature/culture divide—will more effectively prepare the public to critically engage and practically respond to pressing ecological issues such as climate change.
Continue ReadingAbstract: This paper examines the ecologically oriented speculative fiction genre known as “solarpunk” and its value for the cause of environmental justice. This article argues that the status quo is characterized by relative inaction on the issue of fighting climate change and that this inaction is the result of an inability to imagine a “green” future. As a form of speculative fiction which explicitly depicts such green futures, solarpunk may be a valuable tool in promoting action by overcoming widespread cynicism about the future. Solarpunk fiction is thus a useful tool for sustainability educators because it encourages critical examination of one’s environmental impact. This article details the ways in which solarpunk stories function as counter-hegemonic media by intertwining issues of race, gender, sexuality, class, and colonialism with an ecological ethic.
Continue ReadingThis editorial overview provides an introduction to this special Journal of Sustainability (JSE) issue devoted to water and climate change, which is being released during United Nations World Water Day 2020. The article contextualizes some of the water security risks that are exacerbated by climate change, such as increasing floods and droughts. This piece further provides a brief overview of the articles in the special water and climate issue of the JSE.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This article posits that Maasai Indigenous activists’ call to save Kenya’s Mau Forest Water Tower for its ability to protect downstream water security has emerged as an environmental-policy microcosm illustrative of globally surging interest in such Nature-Based Solutions (NBS). Through an analysis of the Mau Forest issue, a series of United Nations Development Programme case studies, and increasing inclusion of NBS for water at recent global policy events such as the United Nations General Assembly and World Economic Forum, this article suggests that a new water infrastructure policy paradigm appears poised to increase implementation of NBS-informed by Indigenous and Traditional Ecological Knowledge (ITEK). The potential of this paradigm shift is illustrated by the North American Indigenous Mi’kmaq concept of Two-Eyed Seeing, which encourages the synthesis of solutions from both western-emanating Scientific Ecological Knowledge (SEK) and ITEK on a path toward positive social-ecological outcomes.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Part Two of a two-article series describes water conservation through graywater use and rainwater harvesting. Sustainable methods of heating water for a recirculating shower, and potential methods for water filtration and purification are presented. Also addressed is the feasibility of sustainable showering alternatives. An opportunity for educators and students to collaborate in the development of an off-grid recirculating shower is provided as well.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Part One of a two-part article outlines a brief history of showering and questions current showering practices. Current global levels of water use and availability are discussed, plus water use in the United States, relative to Americans’ frequency of showering. The energy requirements for cities to provide clean water is outlined as well as the carbon dioxide emissions that are subsequently released during water delivery and wastewater disposal. In Part Two, water conservation through graywater use and rainwater harvesting is described, and sustainable methods of heating water are offered. Possible methods for water filtration and purification are presented. The feasibility of alternatives for a more sustainable shower is addressed. Both articles conclude with an invitation to students and instructors to collaborate with the author to construct a prototype of an off-grid recirculating shower.
Continue Reading
Anthropogenically-induced water quality issues are plaguing the people and environments of Southwest Florida. In 2018, nutrient-rich runoff into waterways caused one of the largest and longest occurring algal blooms in the area; however, many were unaware or misinformed about the causes or impacts of these blooms. Young people are at the forefront of this changing environment and will continue to face water reliance issues in the years to come (Leal, et al., 2015). However, gaps within the existing science curriculum do not address the anthropogenic actions that are leading to these crises (National Research Council, 2012). Southwest Florida is being drastically altered by the large number of people who move to the area each year; urban sprawl, habitat loss, and human-induced climate change are impacting the region (McVoy, et al. 2011). Local water quality issues necessitate a more focused, specific effort to build awareness and knowledge to ensure clean and safe water is locally available. Therefore, the need for Environmental Education (EE) is becoming increasingly important for students to be able to make informed decisions about personal actions contributing to these issues. The project, Future Leaders of Water Quality (FLOW) focused on educating teachers and students by engaging them in environmental literacy, specifically focused on water quality education in local middle schools. Project FLOW worked with local teachers to develop an innovative, five-day, lesson plan focused on the causes and implications of anthropogenically-induced eutrophic conditions. Data were collected throughout the implementation to measure the impact of the curriculum intervention that addressed water quality issues of the region. The results of the study suggest exposure to the lessons increased student understanding of water quality issues and motivated students to take personal action to improve water resiliency within their local communities.
Continue Reading
Formal educational models are overemphasizing standardization and therefore underestimating the benefits of place. Place-based education is under researched within the field of educational studies and this article attempts to tackle this divide. This article unpacks the definition of place-based education while exploring its relevance to virtually any educational situation. Additionally, a framework for application of place-based education is offered. The proposed framework is supported by a description of its benefits. The idea of a watershed is used to further contextualize the discussion. Recognizing the importance of maintaining the health and integrity of our watersheds is a vital part of a strong sustainability-oriented education program. The reverence and respect for a watershed must be embedded within an ethic which embraces the value of all life on this planet and place-based education is one way to cultivate this reverence and respect.
Continue Reading
While sustainability is often perceived from a framework of fear, emergent understandings of sustainability are rooted in pedagogies of hope. In particular, radical hope, or critical-transformative hope, is transforming sustainability. Radical hope is contextually dependent and is made meaningful when in action. Collective movements such as the buen vivir social movements and transition movements are realizations of radical hope in praxis. Overall, this paper aims to demonstrate that through a multiplicity of movements, sustainability is in the process of continual becoming.
Continue Reading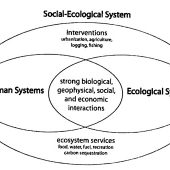
Breaking though to millennials in the classroom is becoming an important objective for all educators. These students demand more from their learning experiences and many traditional education techniques are often ineffective. One technique that holds potential is “Flip” education, a unique active learning approach. Although Flip is normally associated with the hard sciences, this paper presents a case study that demonstrates its effectiveness in the social sciences, specifically an upper division undergraduate environmental/sustainability planning class. Two important takeaways from this study include: 1) that teaching must be more student-centered, allowing students to take more control of their own education as assigned material be available before the fixed class time so as to allow class time for more active learning; and 2) Students report improved learning when Flip experiential methods are used in conjunction with some form of standard professor lectures.
Continue Reading
Abstract: The impact of school gardening on nutritional attitudes and behavior regarding purchase and consumption of food is explored with pupils who participated in school gardens. The researchers of the recent study conceptualized a framework of potential factors influencing nutritional behavior based on empirical data with pupils from general and vocational high schools in Vienna. Three hundred and sixteen pupils, aged between 16 to 21, were interviewed in a cross-sectional study. The pupils who participated in school gardening are significantly better informed about sustainability than the pupils who did not. There is a significant difference between pupils who took part in school gardening and those who did not, regarding their self-assessment towards their connection to nature and sustainability. The total consumption of vegetables has increased within the families of participating pupils by 17%. School gardening seems to promote pupils’ reflection on their own diet as well as foster a favorable attitude towards a healthy and sustainable diet. We conclude that the implementation of school gardening has a significant positive impact on pupils’ attitude and behavior towards sustainable diets.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Students are transformed when they realize that their theory-based actions have real and meaningful impact. Student learning outcomes are enhanced when they realize this impact. This is important, because the topic of sustainability involves a huge amount of grim data about the state of the planet and our impending demise; and an urgent call for action to make positive impact. To enable my MBA students to take action, I designed an experiential, action-research and transformational pedagogical approach; and a mixed-methods study to assess if/ how students engaged with, and learned or cared about sustainability when it was delivered at the level of personal impact and personal action. I found that making sustainability personal did not cause alienation, but did significantly contribute to learning and caring in all students in the course. However, students’ comfort with uncertainty moderated their perceptions of learning, which provides insight for how to improve the course in the future.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Household composting is a practical sustainable behavior which should be further investigated. The Short Composting Survey was developed for use during the Compost Project pilot study to measure the knowledge, values, barriers, and social norms surrounding composting (n=25). The purpose of this research was to describe the testing and refining of the survey tool for the pilot study. Statistical analyses included calculating the Index of Item-Objective Congruence (IIOC) values and conducting a confirmatory factor analysis following administration of the survey. Nine respondents assisted with survey tool development by completing the IIOC, and values ranged from 0.29 to 0.66 which indicated that all of the survey questions matched more than one construct. The factor analysis resulted in a three-factor solution with a cumulative loading of 71.2%, meaning that these identified factors contributed 71.2% of the variance in responses. Factor 1 (“Values”) proved to be the strongest factor, explaining 36.6% of the variance, whereas Factor 2 (“Social Norms”) explained 20.04%, and Factor 3 (“Barriers”) had 14.6%. This survey may be useful for future food composting and sustainability-related research efforts.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Campus agriculture projects are increasingly being recognized as spaces impactful to student engagement and learning through curricular and co-curricular programming; however, most campus farm activities are limited to agriculture or sustainability programs and/or co-curricular student clubs. Thus, campus farms are largely underutilized in the undergraduate curriculum, marking a need to explore the efficacy and impact of engaging a diverse array of disciplinary courses in the rich social, environmental, and civic context of local sustainable agriculture. The Farm Hub program presented here incentivizes instructors to refocus a portion of existing course content around the topic of local, sustainable agriculture, and reduces barriers to using a campus farm as a situated learning context for curricula. A pedagogical framework founded in place-based experiential learning (PBEL) theory was developed to guide instructors in the development and implementation of 4–6-week inquiry-based PBEL modules embedded in existing courses. The framework was converted into a research protocol to quantify program implementation fidelity and PBEL best practice adherence for the proposed lesson plans (intended) and their implementation (applied). The framework enables the development of a cohesive cross-curricular program so that the impact of implementation fidelity and best practice adherence to student learning outcomes in scientific literacy, place attachment and meaning, and civic mindedness can be assessed and the results utilized to develop a formal farm-situated PBEL pedagogical taxonomy. This framework can be applied to PBEL curriculum in natural spaces beyond campus farms.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Although the Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005–2014) was a period of rapid pedagogical revitalization and innovation, much sustainability education today is still delivered using transmissive and instrumental pedagogies common across higher education. Now that the field has integrated many of the insights from the decade, students and facilitators should continue innovating along themes consistent with the goals of sustainability: transformation and emancipation. Yet, more clarity is needed about pedagogical approaches that will transform and emancipate students, allowing them to become innovators that change existing structures and systems. This paper presents a framework combining four interacting (i.e., complementary) pedagogies (transmissive, transformative, instrumental, and emancipatory) in sustainability education, helping to reify pedagogical concepts, rebel against outdated curricula, and orient facilitators/learners on their journey toward transformative and emancipatory learning. The authors begin by reviewing the evolution of sustainability education and transformative learning theory prior to introducing the framework. The paper concludes with a vision of sustainability education that incorporates contemplative pedagogies as essential methods in a field in need of cultivating hope, resilience, and emergence.
Continue ReadingAbstract: With apparel and textile production finding itself a leader in social and environmental responsibility issues, the call to action to influence purchase intention for sustainable and responsible apparel is necessary to both the environment and humankind. Literature supports the connection between consumer knowledge of social issues within the apparel and textile industry and purchase behavior. Cowan and Kinley (2014) identify attitudes as the strongest predictor for purchasing environmentally sustainable apparel. This study looks at the interjection of a type of popular and accepted medium, film, as a possible catalyst to knowledge and attitude change in millennial consumers regarding responsible apparel. This is an exploratory quantitative research study to explore possible future directions of how to impact sustainable purchase intentions of millennials in a consumer driven society. A total of 128 participants from a large Midwest university took part in the study during spring and fall 2016. This study found that millennial consumers had significant change in their purchasing behavior regarding responsible apparel. They also considered themselves more knowledgeable regarding the topic. However, their change in attitudes was not towards being more concerned with what was happening in the industry nor their willingness to sacrifice price and style for responsible apparel.
Continue Reading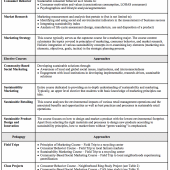
Abstract: As noted by a growing number of marketing scholars, the importance of educating marketing students on sustainability should be an important objective for marketing educators and business schools alike. The focus of sustainability-based marketing education is on the greater good of the environment and society, while adjusting internal and related external processes to sustainability principles. In this conceptual paper, we adopt a broadened definition of sustainability distinct from the narrow understanding of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) adopted by the business world in general and make recommendations for using this broadened definition to reframe marketing curricula and pedagogy. We give specific examples of assignments and pedagogical approaches for four core marketing courses as well as four marketing electives. By doing so, we hope to foster a new marketing mindset and a new generation of marketing practitioners who embrace, internalize, and practice sustainability holistically.
Continue Reading
Though often considered an area of importance and emphasis, the enactment of Environmental Sustainability Education can vary considerably across schools and settings. This study used a narrative approach to tell the story of Environmental Sustainability Education at three schools within a 10-mile radius of our institution: a public charter school, a public school with a magnet STEM program, and a private Friends school. Our findings are discussed using the NAAEE’s Essential Underpinnings of Environmental Education, and shed light on possible future direction for pre- and in-service teacher education in Environmental Sustainability Education.
Continue Reading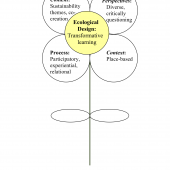
Although sustainability has become an important focus in higher education, there is a need for understanding how sustainability competencies can be cultivated in college and university courses and programs. This article argues that learners who are to become capable of affecting holistic sustainable change, transforming values and culture, healing the earth and human communities, and designing creative solutions, must have the opportunity to engage in learning processes that reflect these learning outcomes. We outline key elements of sustainability pedagogy and suggest best pedagogical practices for designing engaging and holistic sustainability learning.
Continue Reading
This paper presents best-practices for client-oriented project based learning (PBL) based on building audits used to impart practical sustainable engineering skills. Insights were gained over years of natural reflective practice during which students conducted off-campus building audits for the New Jersey Department of Military and Veterans Affairs. Few studies have explored the use of off-campus building audits with real clients in project based learning courses. A survey of students from recent semesters, plus tangible outcomes, are used to evaluate success. The building audits are valued by students and clients. Best-practices contributing to the success of the building audit course are described which can be used by any PBL practitioner. Critical best-practices pertain to training, deliverables, a report template, a submit-review-resubmit cycle, and regular interaction between undergraduate students, graduate student, faculty, and client staff. In particular, repeated cycles of submitting reports, getting comments, and resubmitting appear to be vital to both student learning and client satisfaction. On average, student teams submitted their major report 3.75 times and received comments 3.9 times.
Continue ReadingReynolds (2004) says we write from where we are (p. 53). What does that mean? In a class called Composing our City, place, place-based learning, and place-based projects were the sustainable modus operandi. We wrote, thought, and created where we are from. As we engaged in place-based learning, we touched on topics like the emotions places evoke, how environments come with a sense of place, learning the art of flaneurism, and how crossing borders in our assignments teaches us aspects about our environments and ourselves we could not learn otherwise. Flaneurism was our method of collecting data and the object of our writing, as we explored, described, and discovered where we are from.
Continue Reading
Abstract: This theoretical and conceptual article explores the connection between systems design in education, specifically curriculum design, and critical pedagogy, the educational adaptation of critical theory. The author presents the well-established concept of how the industrial standardization of education stems from the imposing of linear structures onto curricular design, inherently suppressing students and communities to have greater control on their educational experience. While there have been great gains in sustainability education, it is self-defeating to the systems thinking nature of sustainability to have sustainability instruction follow traditional linear formats. The author discusses some essential concepts to systems thinking and systems design, and then explores many of the preeminent authors of critical pedagogy and their respective viewpoints. In the discussion, the author interweaves how a systems approach to curriculum design can help meet calls made by critical pedagogy theorists, possibly alleviating some of the oppressive curricular norms assumed by industrialized linear education.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Two tiny houses were constructed for the homeless at Dignity Village, Portland, Oregon, by Portland Community College students in two sustainability courses over 6 terms, using different approaches. By engaging the business community at large, various non-profits, parents of the students, and residents of the homeless village, the idea of community-based learning (CBL) was embraced by the instructor. CBL created an environment in which lack of experience and wide cultural variation were transformed into a cooperative community of inspiration.
Continue Reading
Abstract: In this article, we discuss the importance of Indigenous traditional ecological knowledge as the foundation of sustainability education, and we describe the need for, and successful efforts to, begin building an Indigenous Traditional Ecological Knowledge initiative at a research university. We share the guiding theoretical framework of our work, and the three goals of the initiative. We note the tensions involved in crafting a vision statement that a diverse group of faculty, staff, and students can all uphold in our collective work. We conclude with a description of our next planned steps for the initiative, and our hopes that this work will help decolonize sustainability education.
Continue Reading
Many educators teach the topic of sustainability, but how many do so in a sustainable manner? From the requirement of textbooks, to paper for printed syllabi or assignments, higher education is a consumer of resources. The materials of design education, however, expand to include media like trace paper for ideation or foamcore for model making, as a means of communicating ideas. Yet, following presentations and grades, a majority of these physical materials enter the waste stream while digital versions populate online portfolios. Hence, design education provides a unique and transferable lens to explore an inquiry-based collection, documentation, exhibition and repurposing of discarded materials, to render new insights and re- imagine pedagogical practices, wherein learning and deliverables truly reflect the values and discourse of sustainability.
Continue Reading
The purpose of this policy study is to provide to educators and curriculum writers a critical account of the diversity and contestability of the conceptions of sustainability embedded into the policies and processes related to the transformation of K-12 curriculum in British Columbia (B.C.), Canada. First, we examine the different conceptions of sustainability within the context of distinctive socio-cultural paradigms: the industrial, the existentialist, and the symbio-synergetic. Second, we address the following key questions: in what socio-cultural paradigm is the dominant conception of sustainability grounded in new K-12 curriculum policy in B.C. and in which ways does that paradigm question the dominant industrial notion of modernity and development?
Continue Reading
Increased understanding amongst scientists and the general public about anthropogenic impacts in general, and climate change in particular, behooves us as educators to adjust our courses and curricula. “Sustainability” and “green” topics are increasingly being discussed and incorporated, but this should be done with deliberation. We undertook this study to understand attitudes, perceptions, and habits of the student body at Iowa State University, with a focus on environmental knowledge and behaviors. Overall, we found that, regardless of demographic, students appear to be interested in environmental topics, reducing their footprint, and improving the environment overall. But, they did not necessarily want to pay more, nor did they fully embrace personal responsibility.
Continue Reading
Some scholars of leadership for sustainability argue that more research needs to be done on the ‘who’ of leaders, the core drivers of the ‘what’ and ‘how’ of their decisions and actions. This paper looks at a leading US figure in sustainability, Gifford Pinchot, who led the establishment of the US Forest Service, and who devoted much of his career to conserving the natural world for the good of his fellow citizens. It describes the formation of the ‘who’ of Pinchot as an adult leader through a focus on his early learning environment in order to point to some essential and timeless principles for the education of leaders of sustainability.
Continue ReadingHuman beings today are living in times of unprecedented social and ecological crisis, a crisis that is to a significant degree of human making. The impending arrival of the Anthropocene geological epoch gives this crisis a name. As academics with a sense of responsibility for our relationships with planetary kin, the awareness of unfolding crisis calls on us to reach a deeper understanding of assumptions about the world, and of modes of living that these assumptions permit, which have been a human contribution to crisis. Furthermore, the Anthropocene calls us to act upon our new understanding. Taking modern European imperialism as a key generative force in the development of Anthropocene, we provocatively develop the idea in this article that the life-ways and worldviews of Indigenous Peoples colonized by European imperialism – including, potentially, marginalized and suppressed life-ways and worldviews of Indigenous Europeans – may hold critical insights by which to negotiate the Anthropocene and to challenge and change habits of thought and action that have led us to its threshold.
In doing so we outline the rationale behind the Alliance for Intergenerational Resilience (AIR) whose objective is to build social-ecological resilience by connecting and supporting locally based projects for the innovative and renovative co-evolution of social and ecological systems. AIR aims to generate inter-cultural relationships between Indigenous communities and communities no longer considered indigenous to place in order to support more meaningful, life-giving social and ecological relationships for all people. In order to further describe AIR’s objectives and its aspirations, the article draws on the Alliance’s inaugural event, the Elders’ Voices Summit, four days of Indigenous-led sustainability education with more than 100 international participants, representing community, university, government, philanthropy and not-for-profit sectors. We conclude by casting our hopes forward to envisage future re-indigenization work that supports the connection and reconnection of human beings with the Earth and the places of the Earth to which we belong.
Continue Reading
Climate change is a difficult subject to teach because it requires complex scientific understandings and is connected to personal beliefs (Spence, Poortinga & Pidgeon, 2012). It is important to teach students the science of climate change and impact their personal beliefs to produce behavior that will mitigate climate change. In this study pre and post surveys focusing on climate change understanding, belief, and behavior were administered. Interviews were also conducted. The quantitative and qualitative data were conflicting, but through triangulated data analysis learning design elements promoting Climate Change Literacy in higher education were identified. A conceptual model was developed with the learning design elements to improve the teaching of Climate Change Literacy. Findings depicted three design elements that increase students’ Climate Change Literacy: 1) Decreasing students’ psychological distance from climate change, 2) Utilizing students’ sense of place, and 3) Student investigation of their own research questions. Increasing students’ Climate Change Literacy is the critical first step in making sustainable societal transformations required for mitigating climate change, our most pressing environmental issue that impacts all people and the natural environment (Spence, Poortinga, & Pidgeon, 2012).
Continue ReadingAbstract: Using a mixed methodology, we followed the preparation of fifteen teacher candidates through a summer content immersion and schoolyard ecology field experience as part of their alternative route to teacher certification program. The primary purpose of our summer project was to support and learn from the funds of knowledge of the teacher candidates and migrant youth. Next we sought to determine if a learner-centered teaching, modeled in a content immersion that explored the inner life of cells, could be applied heuristically to co-plan and teach schoolyard ecology. The results suggest that a learner-centered teaching translates well between content and field immersions and can positively support the cultural and community wealth of both candidates and migrant youth while affirming and deepening our appreciation of the local natural world.
Continue Reading