Welcome to the February 2017 General Edition of the Journal of Sustainability Education!
Continue Reading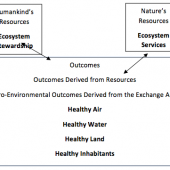
Abstract: In this paper we compare and contrast the Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1985) with Social Exchange Theory (Homans, 1958) as conceptual foundations for eliciting pro-environmental behavior. We reason that Social Exchange Theory provides the better orientation because of its metaphorical power in casting humankind as being in a reciprocal relationship with nature rather than being in a superior position over nature. We illustrate our thinking by discussing ecosystem services (Melillo & Sala, 2008) as nature’s contribution to humankind in return for humankind’s responsible environmental stewardship.
Continue ReadingAbstract: This field experiment investigated effects of a descriptive norms-based sign combined with five footprint sticker decal prompts directing individuals to help save energy by using a revolving door, as opposed to a swing door, to exit a mixed-use building. We found that the percentage of individuals using the revolving door increased in both conditions (weekday and weekend day) after we implemented the sign and decals. Notable considerations in creating descriptive norms-based signage to encourage environmentally responsible behavior in mixed use buildings are discussed.
Continue Reading
Abstract: Finding time for place-based instruction can be difficult using a traditional ground classroom or online format. This is a case study report showing how blending the two modalities can increase opportunities to go more in depth on environmental topics. This blending of both classroom and online creates a sense of place and encourages teaching with multiple learning styles. The increased classroom flexibility allows more individualized instruction for student’s needs and interests. This report will share how an environmental biology class implemented a blended learning class over two semesters. Results of this pilot show an increased student effort by allowing for more varied learning about the local environment.
Continue ReadingAbstract:
This paper describes a role-playing, negotiation “game” based on the Xayaburi Dam in Laos. We have used this activity in our graduate programs as a tool for bringing to life the complexities of decision-making around natural resources, economic development, and sustainability. Over the past several years of using the game in the classroom, we have found it to be an effective means of exposing students to the kinds of opportunities and constraints that different stakeholders face as well as the kinds of communication and negotiation tactics they might use to influence outcomes. We provide background on the real-world situation on which we based the fictional scenario for the game and discuss the learning outcomes we have observed.
Abstract
The study assesses the extent to which curriculum of secondary schools in Tanzania addresses sustainable education through integration of environmental education. Specifically, it evaluates the subjects used to deliver environmental education in secondary school. Also the study found out perceptions, challenges, and recommendations for implementing environmental education. This research adopted a case study, qualitative approach to study the subject matter in its natural settings while making sense of the contents of the subjects and perceptions of stakeholders. Cross sectional, stratified sampling involved both students from all classes, experienced teachers in geography and biology and a head teacher as well. It was found that most environmental education competencies are delivered mainly through the geography subject, and some in biology using an integrated teaching approach. Students and teachers were fairly knowledgeable and had understanding of basic environmental issues. Main challenges facing implementation of environmental education included an integrated learning approach, inadequate knowledge on environmental education, lack of support from each other and from school administration, and cultural myths and beliefs.

Abstract: The aim of this case study was to develop, apply and evaluate a science-education workshop format to communicate climate change to young people. Based on current theory in climate change communication and Education for Sustainable Development, the workshop has been applied in different contexts with more than 300 children and teenagers. A specification of the consecutive steps should help practitioners to use the workshop in their contexts. While results of the application of the workshop should give an insight into what can be expected from the workshop, an impact assessment of the participants who took place in the workshop outlines the effects it has on students. This paper does not only provide hands-on advice on how theoretical climate change communication knowledge can be translated into action, it also outlines the impacts of the described workshop.
Continue Reading
Abstract: As native Midwestern prairie and savannah landscapes continue to be destroyed, some environmentalists are working to reconstruct the prairie and savanna ecosystems that greeted European settlers a century and a half ago. This series of photographs engages those reconstructed landscapes and considers the fundamental question of what we consider natural. As many of these sites are used for educational and scientific purposes, this series also engages how the arts can contribute to our understanding of place.
Continue ReadingAbstract: This thought piece proposes the adoption of a new “3 Rs” to inform a climate-responsive environmental and sustainability education (CRESE): reclamation, resilience, and regeneration. As a changing climate becomes the larger campus of our learning, denial and top-down emergency preparedness both prove to be insufficient. We are invited into a deeper approach. Reclamation and resilience fold in (1) the saving of enduring biocultural lifeways and patterns and (2) the dynamic flux-states of panarchic socioecological resilience models. These two partner with (3) regeneration: context-responsive social collaborations; eco-socially-embedded capacity building systems; and the promise of regenerative design. These three approaches allow us to re-envision educational systems and encounters that are proactive rather than only reactive or responsive in metabolizing persistent climatic volatility. These three approaches – reclamation, resilience, and regeneration – echo the three approaches to climate change that Pelling has suggested (2009) – mitigation, adaptation, and transformation. Note, however, unlike Pelling’s model, these approaches are conceived as simultaneously requisite literacies and movements rather than as competing. Reclamation, resilience, and regeneration represent ever-more-complex types of capacities and support capacity building aimed together toward life-supportive, dynamic, complex systems transformations. Environmental and sustainability education that fosters skills of reclamation includes preservation, conservation, recording, and the establishment of libraries and sanctuaries of exemplar systems. Environmental and sustainability education (ESE) for resilience includes network extension and adaptive capacity building. ESE for regeneration nurtures emergent complex systems metacognitions, creativities, and transformative, transgressive social approaches that are connective, disruptive, and innovative and model and embody complex emergence. Regenerative ESE fosters skills to facilitate catalysis of emergent regeneration, self-organization, and transformation into more complex living systems. All of these position embedded learners in pro-active, systems-intensive embodiments of the types of living networks that foster survival, flexibility, thriving, and phase-change during our entry into a time of consistent climate turbulence.
Continue Reading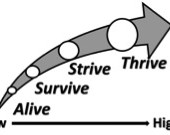
Abstract: A conceptual sustainability taxonomy has been needed to better communicate the value of sustainability, to align sustainability scholars’ theories and sustainability educators’ practices, and to develop curriculum, teaching, learning, and assessment to enhance college students’ comprehension of and commitment to sustainability across general, major, and co-curriculum. Original conceptual research, including the grounding of a conceptual sustainability taxonomy with early career student affairs educators in higher education, presents a grounded conceptual sustainability taxonomy (Alive, Survive, Strive, Thrive) for educating college students and initiating scholar-practitioner contemplation, discussion, and research.
Continue Reading
We report an evaluation of a place-based education (PBE) teacher professional development program that aimed to understand the perceived impact of PBE on students and teachers, constraints to implementation of PBE in schools, and strengths and limitations of the professional development program, as identified by teachers. Nine teachers, the full 2014 cohort of participants in Wilderness Inquiry’s PBE professional development program, completed a written reflection exercise and were interviewed following the implementation of a PBE lesson or unit developed as part of their professional development program. Findings indicate that teachers perceived PBE to have several important impacts on students, including stronger engagement in learning, enhanced collaboration, and heightened significance for the concepts learned. Teachers also perceived impact on themselves, including professional growth, sense of fulfillment and an expanded repertoire of teaching approaches. However, there were perceived constraints to implementing PBE, including support from peers and administrators, time, money, weather, and the composition of the class. This research adds to a growing body of research reporting positive impacts of PBE. Teachers’ feedback on the professional development program highlighted specific aspects of an effective professional development program. An enhanced understanding of the benefits of and challenges to PBE and program characteristics that maximize teachers’ time at a professional development program will help educators and curriculum developers to better support, develop, and encourage the implementation of PBE in standardized curriculum.
Continue Reading